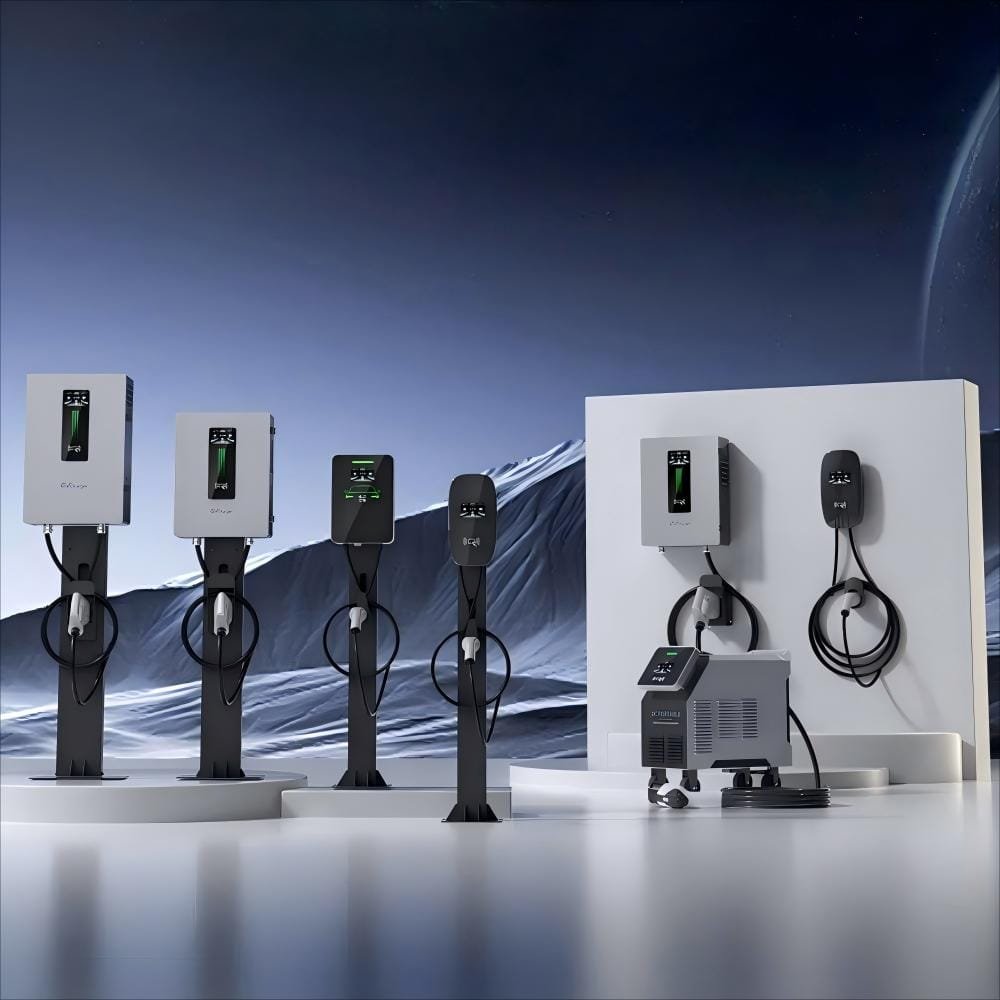
As the electric vehicle (EV) market rapidly evolves, the development of charging infrastructure continues to improve. Understanding the different types of electric vehicle chargers is essential for both current owners and potential buyers.
Electric vehicle chargers are primarily divided into three categories: Level 1 , Level 2 , Level 3 ,Level 4, Each type is suited for different scenarios and needs.
- Characteristics: Level 1 chargers typically use standard household outlets (120V), providing a low charging power.
- Charging Time: Depending on the battery capacity and charging power, charging may take over 8 hours. This type is ideal for overnight charging.
- Use Cases: Best for users with short daily commutes who can charge at home or work.

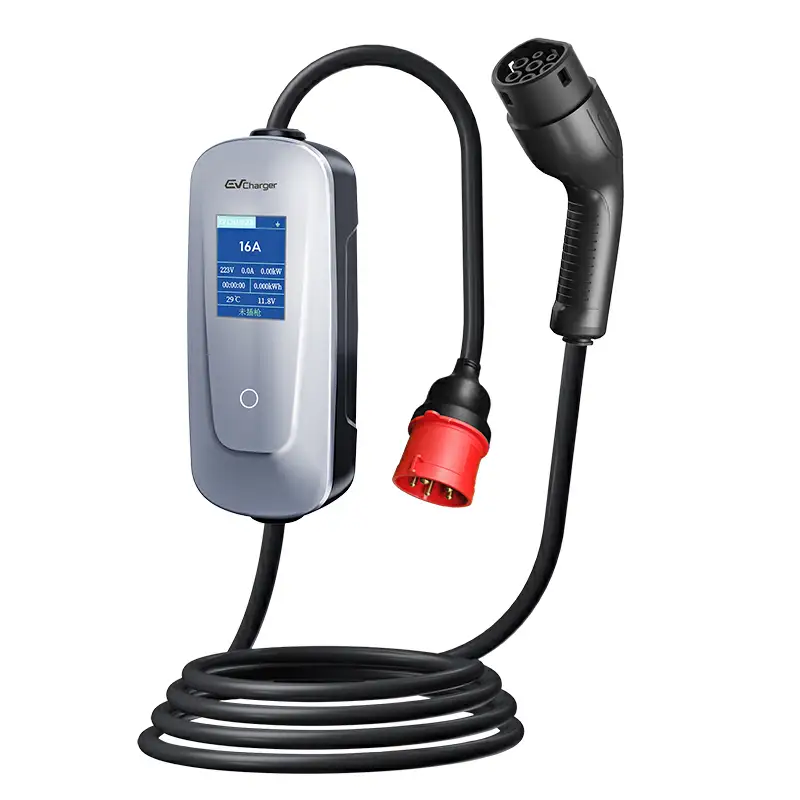
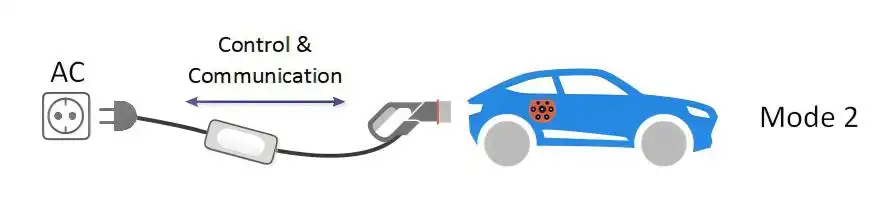
- Level 2 charging requires a special cable with integrated protection against AC and DC shocks. In mode 2 charging, the charging cable is supplied with the EV. Unlike Mode 1 charging, Mode 2 charging cables have built-in protection against electric shock. Mode 2 charging is the most common mode of EV charging today.
- It is AC charging via a domestic or industrial socket with integrated protection on the charging cable.
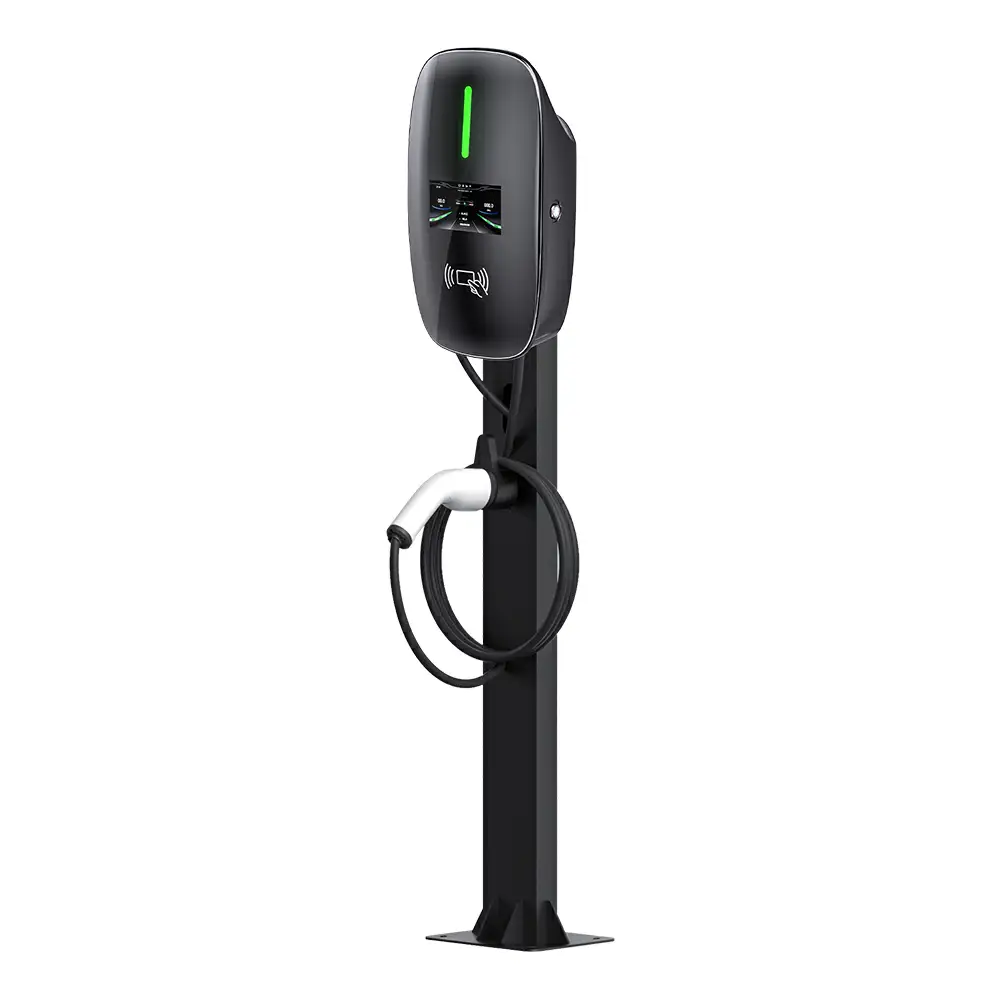
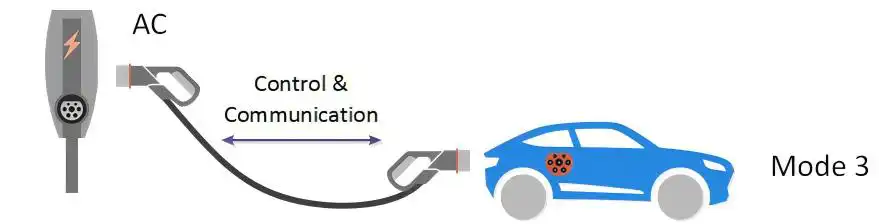
Level 3 charging involves charging an electric vehicle using a dedicated charging station or a home wall-mounted charging box. Both provide shock protection against AC currents. In Level 3, the connection cable is provided by the wall box or charging station and the EV does not require a dedicated cable for charging.
Level 3 charging is currently the preferred method of EV charging
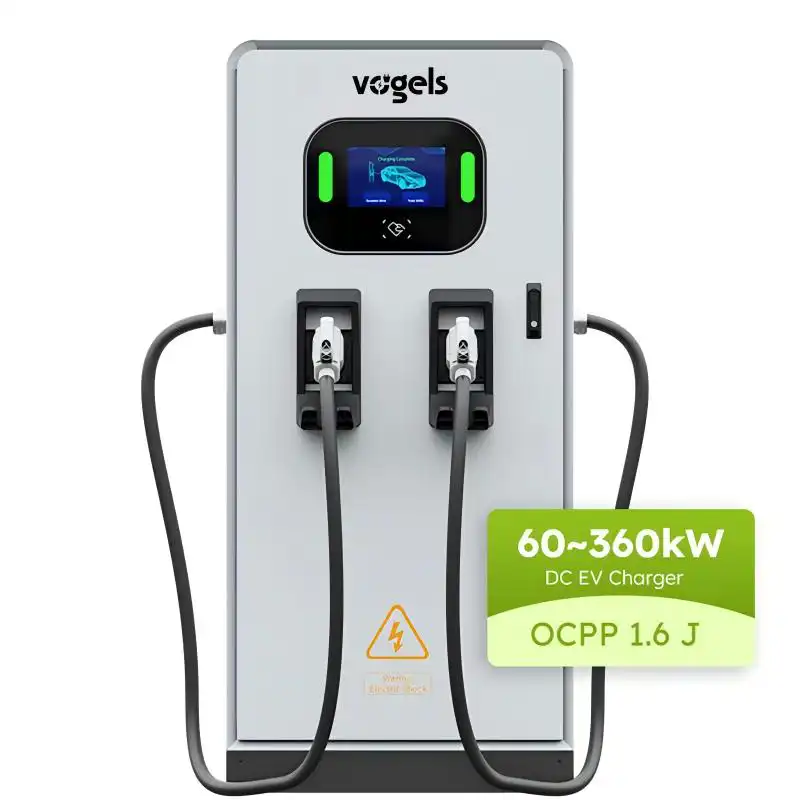
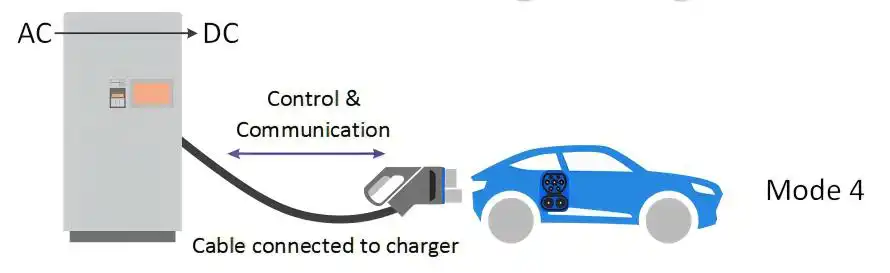
- Characteristics: Level 4 chargers use direct current (DC) and can provide high charging power of up to 380 kW or more.
- Charging Time: Extremely fast charging, typically allowing for an 80% charge in about 30 minutes.
- Use Cases: Perfect for service areas along highways and for long-distance travelers who need quick power boosts.
Different electric vehicle brands and models may use various charging connector standards. Common standards include:
- Type 1 (SAE J1772): A widely used AC charging standard in North America.
- Type 2 (Mennekes): The predominant AC charging standard in Europe.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): A versatile standard supporting both AC and DC charging, increasingly adopted by new models.
- CHAdeMO: A DC fast charging standard primarily used by Japanese brands.
Selecting the appropriate charger and connector type is crucial for electric vehicle users. Factors to consider include:
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure that the charger is compatible with your electric vehicle.
- Charging Environment: Choose a charger type based on where you’ll be charging; home users may opt for Level 1, while long-distance travelers may require Level 3.
- Installation Requirements: Some chargers need professional installation; users should consider the electrical capacity and wiring conditions of their home or business.
As electric vehicle technology continues to advance, charging technologies are evolving as well. Future trends may include:
- Wireless Charging: Research and development of wireless charging technologies for more convenient charging experiences.
- Ultra-Fast Charging Technologies: Further enhancements in charging speed to reduce waiting times.
- Smart Charging Networks: Utilizing IoT technologies for intelligent scheduling and management of charging networks.